What is the Cloud and Why is it So Important?
Simply put, the ‘Cloud’ is computing power and data storage on the internet.
Cloud computing power is a commodity that can be circulated on the internet, in the same way that water or electricity can be efficiently distributed via a network of pipelines or wires.
To better understand how the cloud works, let’s think about how electricity works in our house. When moving into a new house, the first step is to find an electricity supplier and sign a contract with them. Once the electricity is connected, it will be available for use in different ways. By connecting the electricity to different appliances, electricity can be used to cook or to cool the room. Depending on the budget, the air conditioner can be used overnight on a hot day, or turned off and open the window to save usage and costs. Electricity is billed based on a small connection fee and the energy usage of the household.
Similarly, the computing power of the cloud is available via the internet. But instead of electricity, the products are the processors, memory, network, storage, and applications. Cloud computing allows you to store, manage and process your business data on virtual servers. The computing power required to store and process your data is supplied based on demand, and you don’t need to invest or maintain the infrastructure.
Why is the cloud so important to business?
Compared to traditional IT solutions, cloud computing has several major advantages. These advantages allow businesses to complete core commercial activities better and faster, such as personalised pricing, improved targeting, predictive outcomes, automation of reporting and more accessible data structures.
- Relative Low Cost: cloud computing eliminates the need for running on-premise data centres which are very expensive and often unaffordable for smaller businesses.
- Data Security: the large cloud computing service providers (Amazon, Microsoft, Google) can provide industry-recognised, high standard security and governance to secure your data.
- High Reliability: this is one of the most important advantages of using cloud computing. The high reliability and availability of cloud computing ensures businesses have confidence in providing uninterruptible services.
- Elastic Scalability: cloud computing allows the computing resources to be quickly scaled up to meet increased traffic, or scaled down to save costs.
- Fast Global Deployment: cloud computing helps businesses improve their end-user experience. Websites, images and videos can be quickly deployed to the geographic locations that are close to the end-users to reduce latency.
- Rich Set of Services: cloud computing offers a rich set of tools and services such as web hosting, machine learning, business intelligence and business insight services to empower your business.
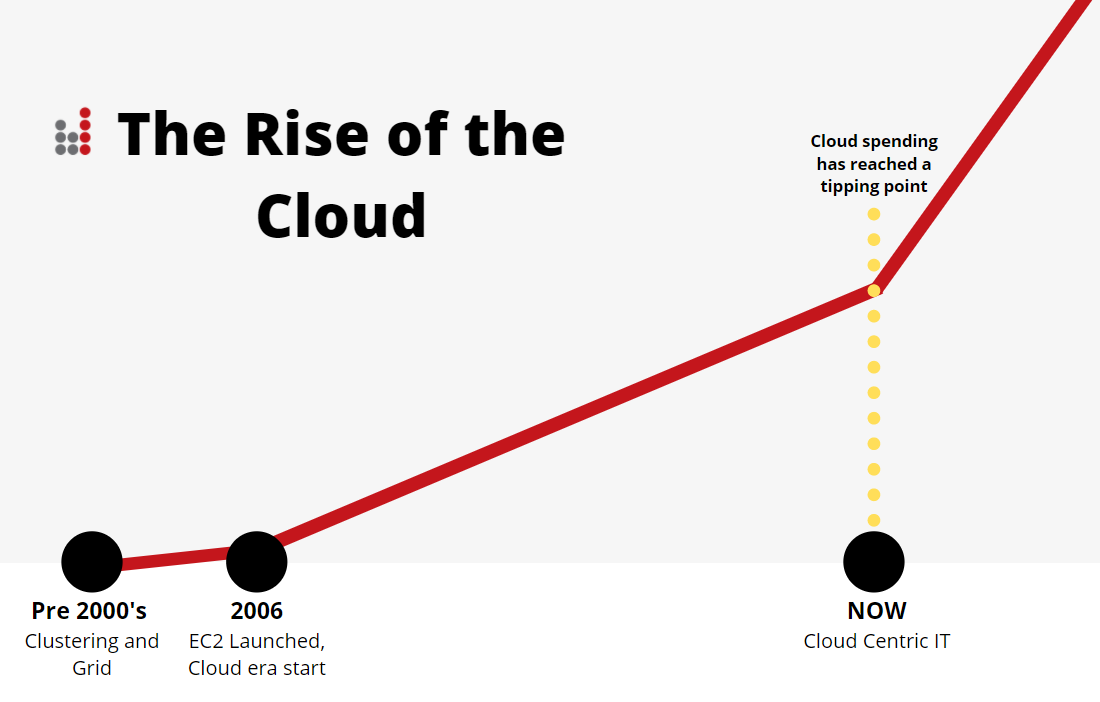
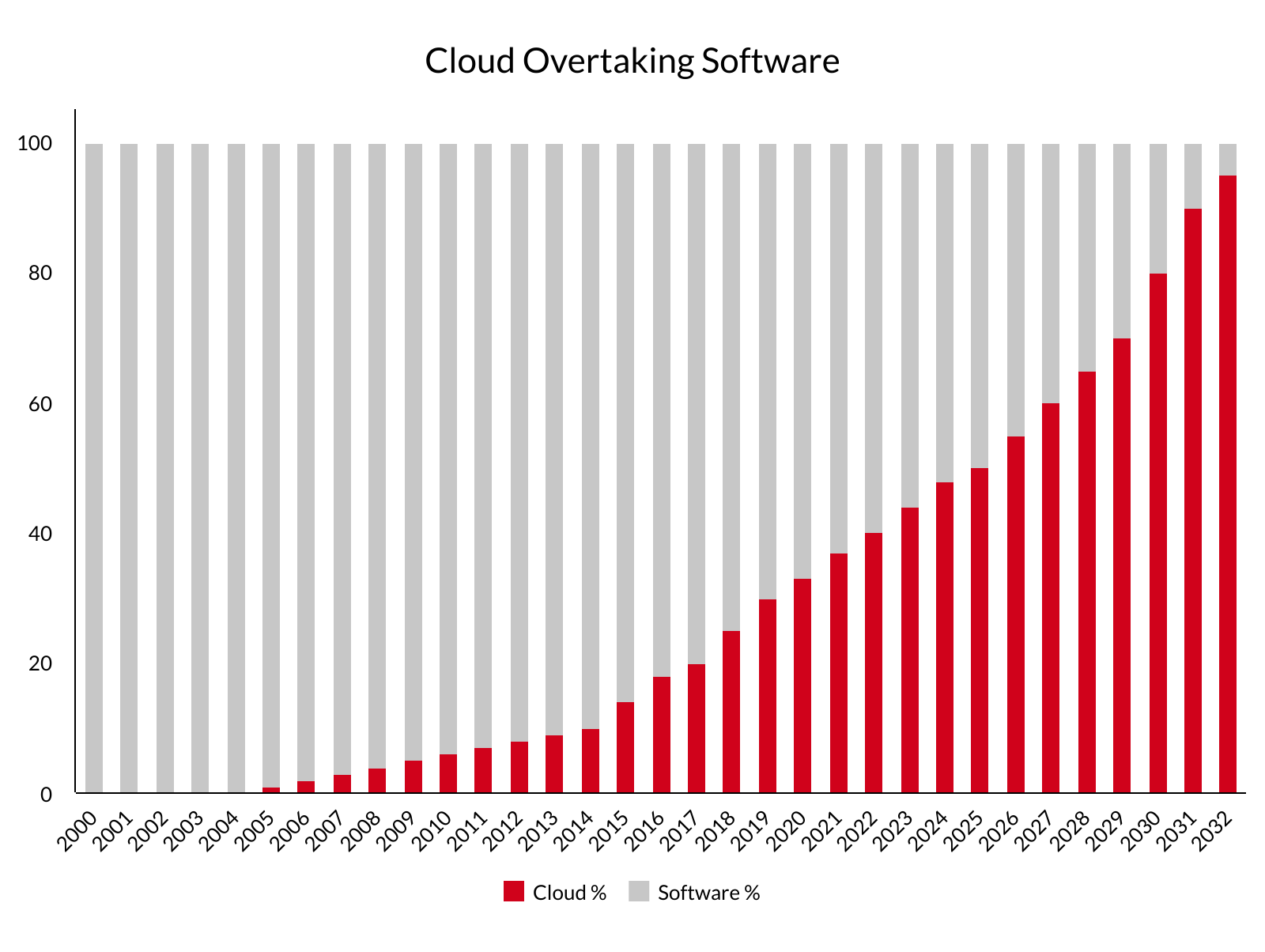
Since Amazon released the first cloud service Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2) on Amazon Web Service (AWS) in 2006, more enterprises have embraced the benefit of migrating to the cloud. The last decade has seen the rapid rise of the cloud economy and this is approaching a tipping point. In 2019, a Gartner survey shows that 10% of the surveyed enterprises plan to close their traditional data centre and migrate to the cloud. 80% of the surveyed enterprises responded that they plan to close their traditional data centre by 2025.
So what does this mean to your business?
This implies that the cloud economy is approaching (or has already passed) the tipping point. The cloud economy will be the next big thing and if businesses fail to migrate to the cloud, they may miss the exponential growth opportunity as their competitors leave them behind.
Cloud Service Models
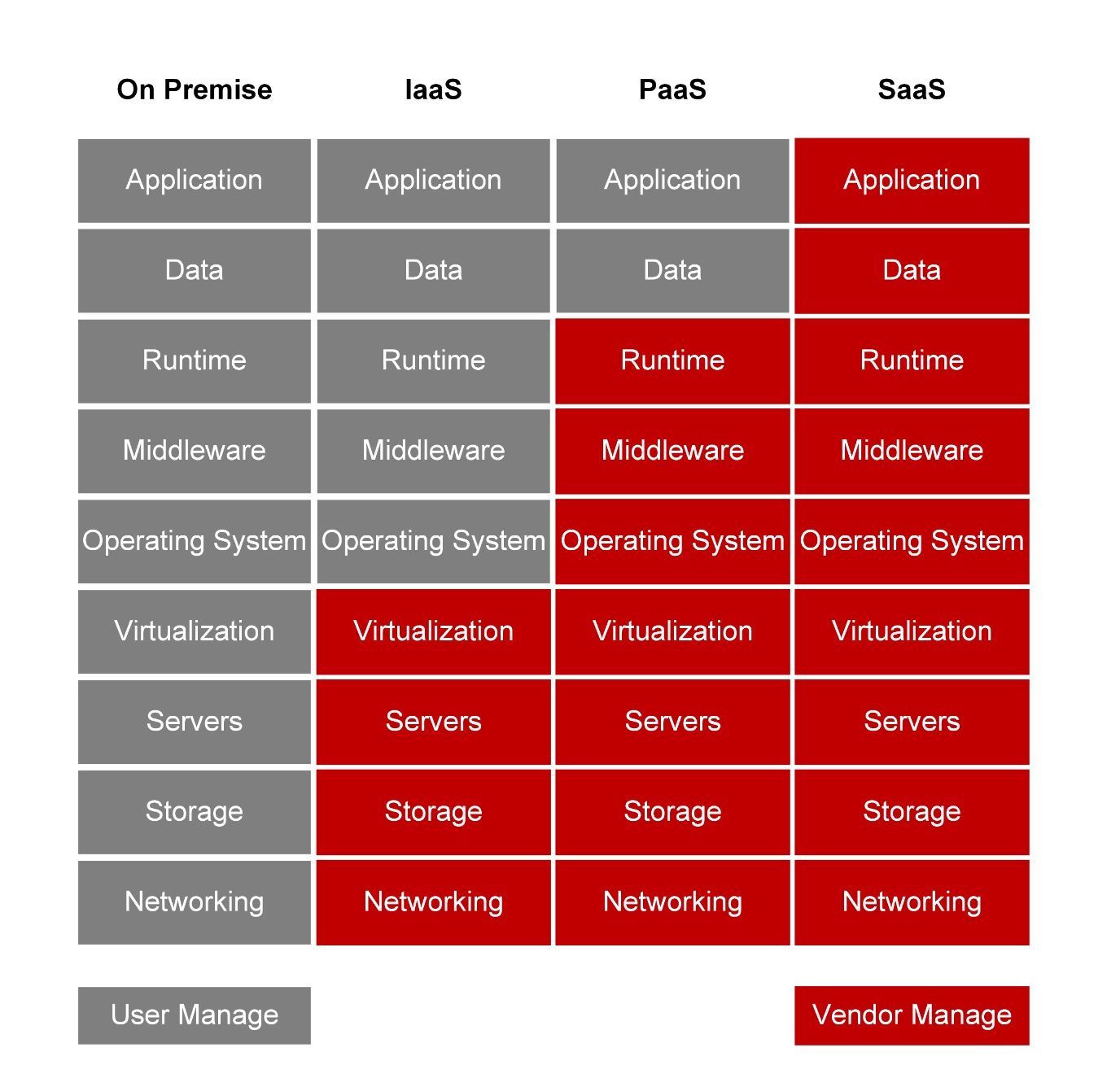
So how to choose the cloud computing service that suits your business? There are 3 main cloud computing service models, these are IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS is the delivery of computing infrastructure as a service; this provides the virtualisation of computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides an on-demand development environment for developing, testing, and maintenance of software applications. PaaS delivers not only the infrastructure but the middleware such as database, messaging engines, and solution stacks.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Under the SaaS model, application software is hosted and managed by the cloud service provider on a cloud infrastructure. End-users access the application over the internet.
The table below shows the resource management responsibility of the different service models.
What’s next?
It’s time to consider cloud computing to be the next step in advancing your company IT systems and data storage. At Forecast we specialise in designing and implementing cloud infrastructure for a wide range of businesses. When you’re ready to take the next step, give us a call.

